Filling in the “Search Gap” of Google Analytics with Google Search Console
3 tips on how to use Google Search Console to optimize your digital experience
One of the major functions of Google Analytics is to help you understand where your website visitors are coming from.
Usually, it does a great job of providing you with the details of your performance regarding traffic channels such as social media, referral, and paid search. However, this same effectiveness does not apply for organic search.
Due to the privacy policy of Google Analytics, it doesn’t have the ability to collect the search queries that led people to your website. Necessarily, this means that you cannot see your performance on these queries.
That’s where Google Search Console comes in. Formerly Google Webmaster Tool, Google Search Console can help you fill this gap in Google Analytics and help you understand what keyword queries led people to visit your website. It will also show you your performance on these queries.
This article is going to show you 3 tips that will help you use Google Search Console effectively to fill this “search gap”.
How to set up Google Search Console correctly
How to use Google Search Console to complement search analytics
How to use Google Search Console to conduct search optimization
These 3 tips will help you understand how you are performing in organic search, and how you can take actions to improve your SEO and search rankings.
Google offers all of these incredibly powerful optimization tools free of charge, so why not take advantage of them?
Let’s get started.
1. Setting Up Search Console Correctly
Before benefiting from Google Search Console, you need to make sure you set it up right.
While setting up the tool may seem easy at first glance (the official Google instructions are attached here), incorrect setup is the most common barrier to use for the analysts and business owners that I have talked to.
This is because, in order for Google Search Console to return results, you need to set it up using the exact url of your website.
Let’s use Humanlytics.co as an example. The official url of humanlytics.co is https://www.humanlytics.co, and in order to get correct search analytics results you need to make sure you use this exact url.
This means that anything ranging from http://www.humanlytics.co to humanlytics.co will probably pass the setup inspection, but won’t actually provide you with any search results.
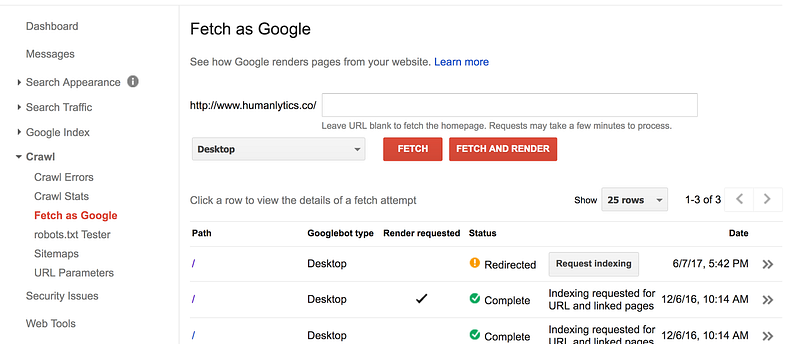
In order to figure out whether your url is setup correctly, you need to go to the “Crawl” -> “Fetch as Google” section of Google Search Console and fetch your homepage as Google.
We changed our domain to the more secure one this year, so you will see both “redirected” and “complete” response
If the status of the fetch is “complete”, you entered the right url. However, if the status reads “redirect”, the url is not correct.
In order to fix this, look at the detailed response of the fetch. In the “http response” section, it will show you the correct url of your website that you should setup for Google Search Console in the “Location” parameter of the response.
In this illustration, the 4th line contain the correct URL of my website
2.Search Analytics
The most straightforward function of Google Search Console is to help you conduct search analytics on queries that led to visits to your website.
Google Search Console not only shows you which query led to the most clicks on your website, it also shows you how many impressions your website had with those queries, your website’s position with those specific keywords, and the click through rate of your website for each keyword.
Beginning last year, it became possible to integrate the search analytics function of Google Search Console with Google Analytics in order to conduct more detailed search analytics such as understanding popular queries in specific countries or on specific devices and understanding popular landing pages for individual queries.
You can find instructions on how to integrate the tools at the link below:
https://support.google.com/webmasters/answer/1120006?hl=en
With these functionalities, you can not only better understand what your target user groups are searching on Google and which lead to your site, but also use information provided here in order to help you pick keywords for both paid search ads and SEO.
You can find all of the features mentioned above under the Acquisition -> Search Console section of Google Analytics.
3.Search Optimization
While Google Search Console is a great tool for Search Analytics, its functionality goes beyond that.
The best way I can think to describe the functionality of Google Search console is to liken it to a portal. Google provides this portal so that you can understand how Google Search views your website to prevent miscommunication.
For this reason, Google Search Console provide you with a wide range of search optimization tools to help you identify the weaknesses of your on-page and off-page SEO performance. This should help you improve your search ranking on the Google search results page.
In general, the tools can be divided up into three categories:
A. Search Appearance
Tools in the Search Appearance section help you modify and customize how your search results show up on Google.
A simple workflow for this function is as follows:
(1) Visit the “Structured Data”, “Rich Cards”, and “Data Highlighter” sections under Search Appearances if they apply to your website and modify their content according to your target customer profile.
(2) Visit the “Accelerated Mobile Page” section and figure out whether the mobile version of your website adheres the coding standard that will optimize its loading speed (read more about AMP here).
(3) Visit the “HTML Improvement” section to identify weaknesses of your website and improve them accordingly.
One function I want to highlight here is “HTML improvement”. This function goes through your website and identifies HTML problems that may cause your website to rank lower than it should on Google. Working through these improvements with your developers can improve your search ranking.
B. Search Traffic
Tools in the “Search Traffic” section are great at helping you understand your current organic search performance.
(1) The “Search Analytics” function, which we looked at in depth in a past series, shows you how your website is performing with regard to various keywords and queries.
(2) The “Links to Your Site” and “Internal Link” functions cover two major factors that Google uses to determine your search ranking. Using these two tools, you can gain a rough idea of how well you are doing with search ranking and plan to improve them if needed.
(3) Lastly, I want to briefly touch on the “Mobile Usability” tool. This tool has recently become crucial to your ranking as Google recently announced that it will consider “Mobile Usability” a major factor when determining your search ranking.
https://support.google.com/webmasters/answer/1120006?hl=en
All functions introduced in this section are meant to be iterative and you should carefully monitor your performance regarding all four functions introduced here when conducting activities such as SEO to understand the effectiveness of your actions.
C. Indexing and Crawling
In order to remain up to date regarding your website Google constantly indexes and crawls it looking for changes. If the Google bot runs into errors or inefficiencies during this crawl process, it will greatly harm your organic search ranking no matter how well optimized your website is.
This final category of tools helps you identify those potential errors on your website so you can fix them as soon as possible.
Below, I’ve laid out a simple workflow to make sure that Google can access all of your websites:
(1) “Visit Google Index” -> “Index Status”, and make sure this number is roughly the same as the total number of pages on your website.
(2) Visit “Google Index” -> “Blocked Resources”, and make sure no resources are blocked (unless you want to block some resources).
(3) Visit “Crawl” -> “Crawl Errors”, and make sure that there are no errors in the past 90 days. Resolve the errors if need be.
(4) Visit “Crawl” -> “Fetch as Google”, and make sure that the way Google sees your website is how you intend it to see it. Modify your website if needed.
(5) Visit “Crawl” -> “Sitemaps”, if you do not have a sitemap published on Google Search console, publish a sitemap of your website using this section. This will help improve your search ranking.
This article showed you three tips that will help you use Google Search Console as a complement to Google Analytics so that you can better understand and optimize your search performance.
While I only addressed a few key functionalities of Google Search Console in this article, using these functionalities well can greatly boost SEO efforts. If you want to learn about any of these functionalities in more detail, feel free to comment below or email me at bill@humanlytics.co. I am more than happy to help you with the tool.
This article is produced by Humanlytics. At Humanlytics, we build tools for SMBs that not only help them answer their business questions and track metrics in real time, but also tell them what questions they should be asking in the first place — all with the goal of teaching them how to implement solutions.
If you are interested in more content like this, please follow us on Twitter,Facebook, and Medium (at analytics-for-humans).